Laboratory Manual
Course: 410
Subject: Practical - Biopharmaceutics-II

Course: 410
Subject: Practical - Biopharmaceutics-II
Prepared By
Md. Imran Nur Manik
M.Pharm
Departmnt of Pharmacy
Uniersity of Rajshahi
Md. Imran Nur Manik
M.Pharm
Departmnt of Pharmacy
Uniersity of Rajshahi
Rajshahi-6205, Bangladesh
Available at
Essential Pharma documents
www.pharmacydocs.blogspot.com
Essential Pharma documents
www.pharmacydocs.blogspot.com
INDEX
Sl. No.
|
Date
|
Name of the experiment
|
Page No.
|
01
|
16.02.12
|
Determination of dissolution rate of enteric coated diclofenac-sodium tablet.
|
2 – 6
|
02
|
19.02.12
|
Determination of dissolution rate of enteric coated aspirin tablet.
|
7 – 11
|
Experiment No. 01
|
Date: 16.02.12
|
Name of the experiment: Determination of dissolution rate of enteric coated diclofenac-sodium tablet.
| |
Principle:
Diclofenac-Na is a nonsteroidal enteric coated anti-inflammatory agent which is commonly prescribed for the relief of pain and inflammation in various rheumatic fever diseases as well as some post surgical conditions. Gastrointestinal disturbances are the major adverse effect associated with diclofenac-Na therapy and thus for oral administration, the drug is usually formulated as enteric coated tablet. Enteric coated dosage forms release drug in the intestine and have been reported to decrease gastric irritation.
When a drug is administered orally in the form of tablet, the rate of drug absorption depends upon the rate at which the drug is dissolved in the GI fluid i.e., the rate of drug dissolution.
Drug in solid dosage form in GI fluid 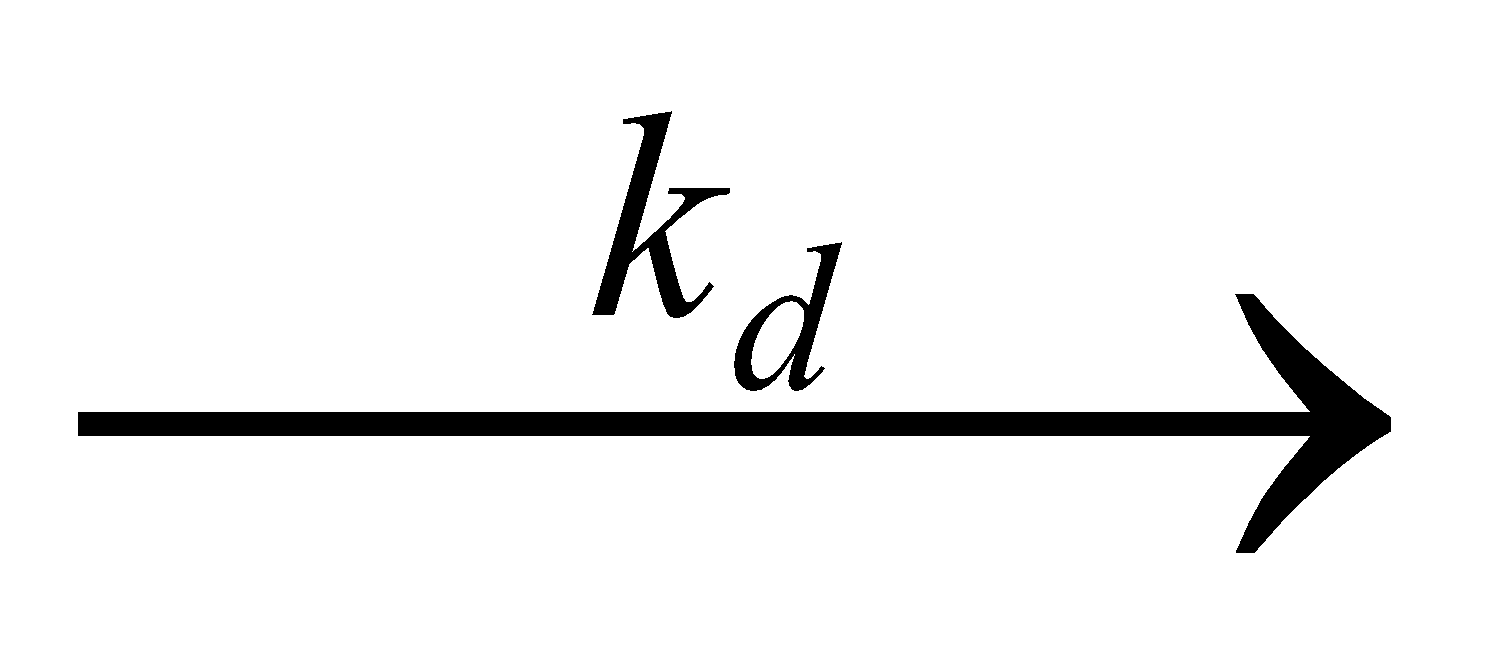 Drug in solution in GI fluid
Drug in solution in GI fluid 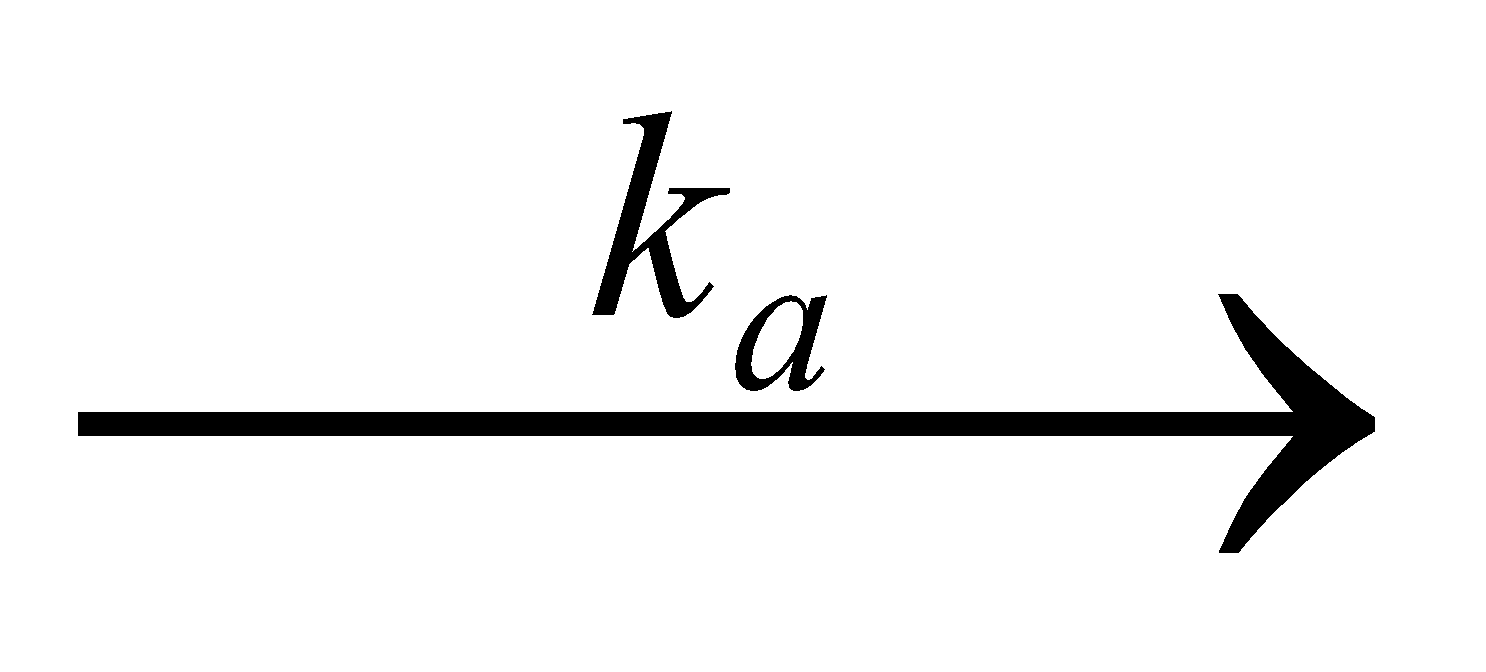
Drug in blood  Elimination
Elimination
Where, kd = Dissolution rate constant
ka = Absorption rate constant
ke = Elimination rate constant
Dissolution analysis of pharmaceutical solid dosage forms have also emerged as a very important test of product quality. The USP has included a test for monitoring drug release from enteric coated table in the gastric simulated fluid (GSF) and intestinal simulated fluid (ISF), which is specified that not more than 10% active ingredient will be dissolved in acid medium (stomach) within two hours and release of drug should not be less than 80% in the alkaline pH medium (intestine) within 45 minutes.
Apparatus:
- USP dissolution apparatus
- Test tube and test tube holder
- Filter paper
- Pipette
- Volumetric flask
- UV-Spectrophotometer (Shimadzu, Model: UV-1200)
Dissolution apparatus: It consists of 1000 ml vessel made of glass or inert transparent material, a paddle with a variable speed motion. For the oral solid dosage form, the motion of paddle is 75 rpm. The vessel can be immersed in a suitable water bath of any convenient size and the temperature is 37 ± 5°C.
Reagents:
- Enteric coated diclofenac-Na tablet
- Gastric simulated fluid (GSF)
- Intestinal simulated fluid (ISF)
- Distilled water
- Standard diclofena-Na powder
Preparation of GSF: 2 gm of NaCl and 7 ml of concentrated HCl were taken in a beaker containing water. The content was transferred to 1000 ml volumetric flask and the volume was made up to the mark by adding distilled water.
Preparation of ISF: 8.05 gm Na2HPO4 and 1.65 gm NaH2PO4 were taken in a beaker containing distilled water. Then the content was transferred in a volumetric flask and the volume was made 1000 ml by adding distilled water.
In the same way another 1000 ml ISF was prepared.
Procedure:
- 900 ml of GSF was taken in a beaker used in the USP dissolution apparatus and other 100 ml of GSF was kept as the stock GSF solution, which was used to prepare the sample-1 and sample-2.
The water level of the apparatus was adjusted. The beaker was kept in place in the dissolution apparatus and the apparatus switched on so that, the temperature of the GSF raises up to 37 ± 0.5°C.
- When the temperature becomes 37.5°, then one enteric coated tablet was put into the beaker containing GSF. The button of the stirrer was switched on to rotate it and the speed of the paddle was adjusted at 75 rpm.
- After 1 hour, 10 ml of GSF from the beaker of the apparatus was taken into a test tube and 10 ml of stocked GSF was added into the beaker simultaneously. Then the beaker was kept in place and let the apparatus to work for another 1 hour.
- The 10 ml GSF taken from the beaker was filtered and 2 ml of filtrate was taken in another test tube and it was diluted to 5 times to make it 10 ml by the GSF stocked. This is sample-1.
- After two hours, another 10 ml of GSF from the beaker in the apparatus was taken into a test tube and by following the same procedure of step-4, sample-2 was prepared.
- The tablet was transferred immediately from the GSF beaker into the beaker containing 900 ml of ISF (other 100 ml of ISF was kept as the stock ISF solution) and stirrer was fitted and allowed to rotate at 75 rpm, temperature was also maintained at 37.5°C.
- After 15 minutes, 10 ml of ISF from the beaker of the apparatus was taken into a test tube and 10 ml of stocked ISF was added into the beaker simultaneously. The 10 ml ISF which was taken then filtered and 2 ml of filtrate was taken in another test tube and it was diluted to 5 times to make it 10 ml by the ISF stocked. This is sample-3.
- After another 15 minutes, another 10 ml of GSF from the beaker in the apparatus was taken into a test tube and by following the same procedure of step-7, sample-4 was prepared.
- Preparation of standard solution:
- 100 ml of diclofenac-Na powder was dissolved in the ISF and made the volume up to 100 ml by adding required ISF.
- 1 ml, 2 ml, 3 ml and 4 ml of solutions from the above solution in step-a were taken into four different volumetric flask (50 ml each) and made the volume up to 50 ml by adding required ISF. Thus, the concentration of the four standard solutions were 20 μg/ml, 40 μg/ml, 60 μg/ml and 80 μg/ml respectively. The concentration of these solutions was used to make a standard curve.
- 10 ml GSF and 10 ml ISF were taken in two test tubes as blank solution.
- Using spectrophotometer, absorbance of all samples, standard and blank solutions were taken at 277 nm.
Data for absorbance calculation:
Concentration of solution (μg/ml)
|
Absorbance (λmax = 277 nm)
|
Blank (GSF)
| |
Blank (ISF)
| |
Sample-1 (GSF after 1 hr)
| |
Sample-2 (GSF after 2 hr)
| |
Sample-3 (ISF after 15 min)
| |
Sample-4 (ISF after 30 min)
| |
Standard-1 (20 μg/ml)
| |
Standard-2 (40 μg/ml)
| |
Standard-3 (60 μg/ml)
| |
Standard-4 (80 μg/ml)
|
Preparation of standard curve:
Taking the values of the four standard solution on y-axis and the values of concentration on the x-axis, a curve was plotted that was found straight line.
Calculation:
From the standard curve, slope of the straight line can be calculated by the following formula: m = 
where, m = slope
y = absorbance
x = concentration
Concentration of drug in GSF after 1 hour: x = 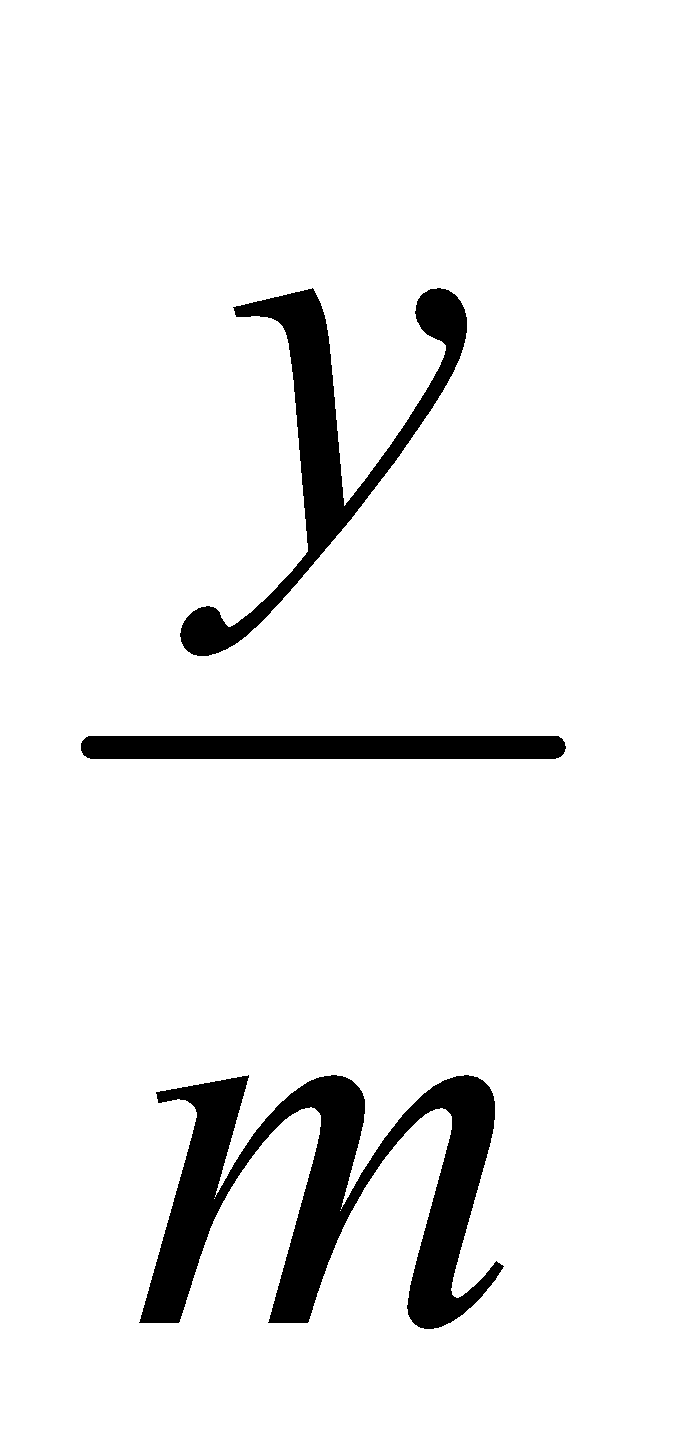 =
=
∴ 900 ml GSF contain = [Dilution factor = 5]
=
=
% of drug release =
Correction value = = μg in 2 ml
= μg in 10 ml
= mg in 10 ml
Concentration of drug in GSF after 2 hour: x = 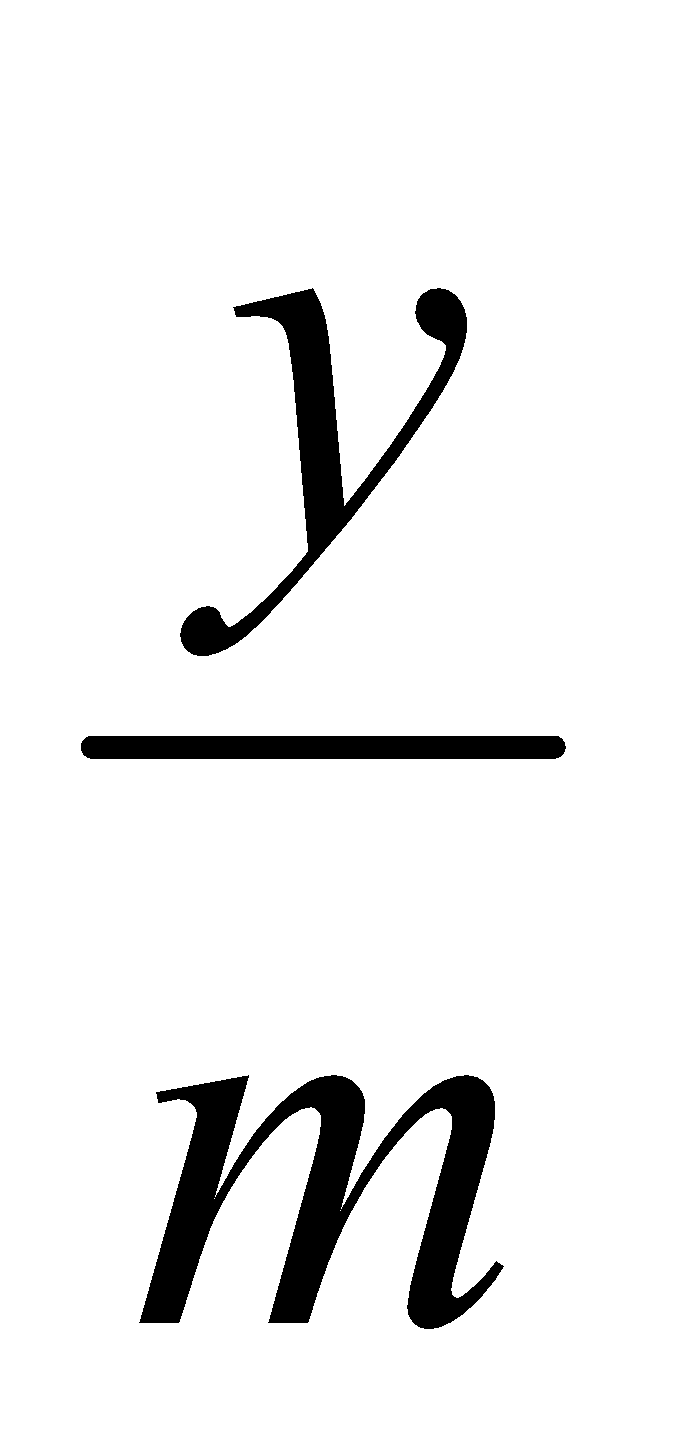 =
=
∴ 900 ml GSF contain = [Dilution factor = 5]
=
=
% of drug release =
Concentration of drug in ISF after 15 minutes: x = 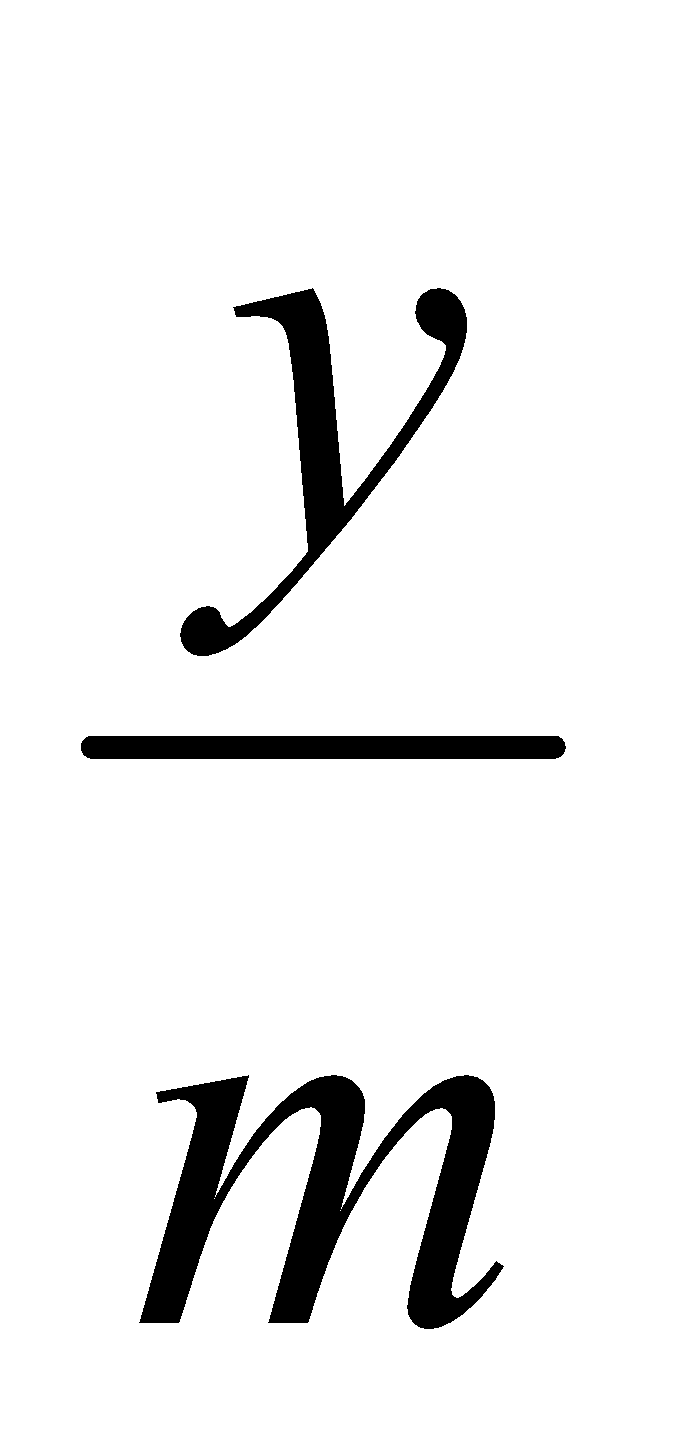 =
=
∴ 900 ml ISF contain = [Dilution factor = 5]
=
=
% of drug release =
Correction value = = μg in 2 ml
= μg in 10 ml
= mg in 10 ml
Concentration of drug in ISF after 30 minutes: x = 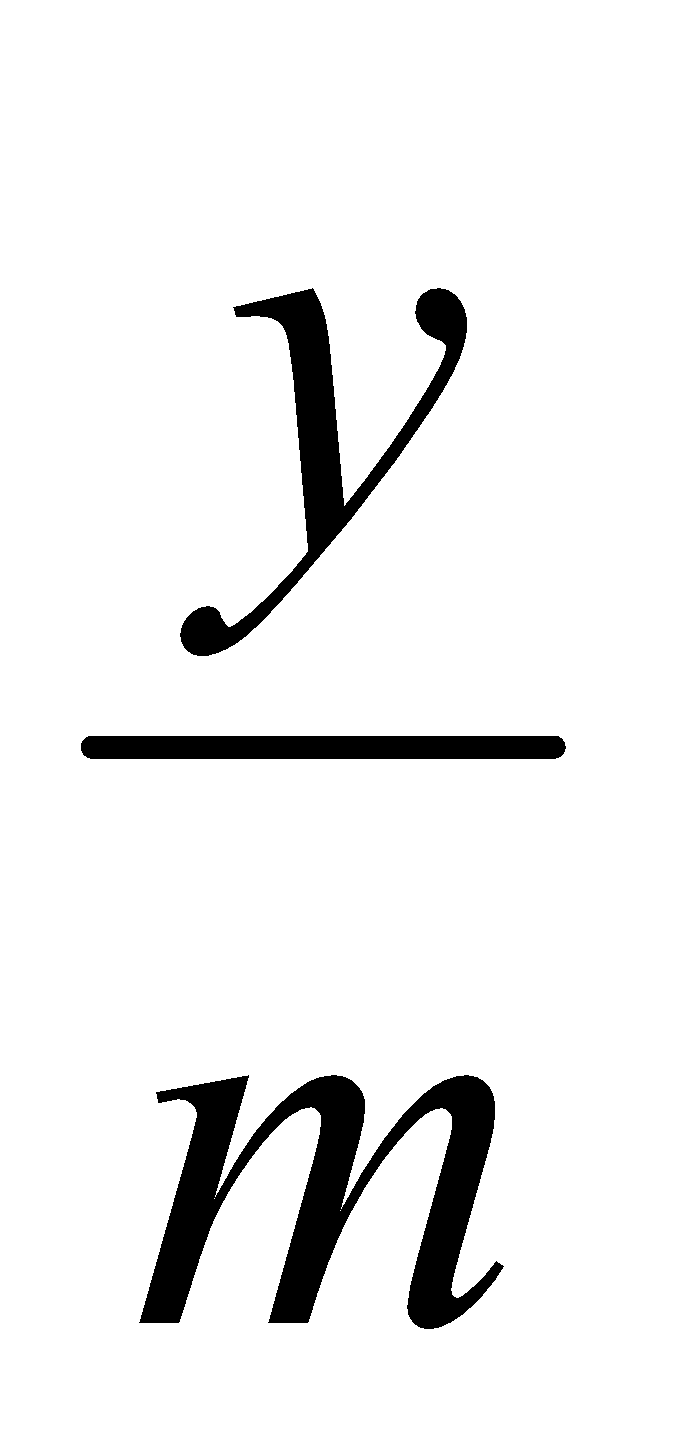 =
=
∴ 900 ml ISF contain = [Dilution factor = 5]
=
=
% of drug release =
Result:
The percentage of release of diclofenac-Na in GSF after 1 hour and 2 hours were and , which are very negligible and percent of release of drug in ISF after 15 min and 30 min were and respectively.
Comments:
Experiment No. 02
|
Date: 19.02.12
|
Name of the experiment: Determination of dissolution rate of enteric coated aspirin tablet.
| |
Principle:
Aspirin is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug. Chemically it is a weak organic acid which has a pka value of 3.5. It is mainly used as analgesic-antipyretic and now-a-days it is also used in cardiac diseases (transient ischemic attack).
Aspirin is a derivative of salicylic acid which is readily absorbed from stomach and upper small intestine yielding a peak plasma salicylate level within 1-2 hours. Gastrointestinal disturbance is the major adverse effect associated with salicylates therapy and for oral administration, the drug is formulated as enteric coated tablet.
Enteric coated tablet dosage forms release drug in the intestine and have been reported to decrease gastric irritation. When a drug is administered orally in the form of tablet, the rate of drug absorption depends upon the rate at which the drug is dissolved in GI fluid i.e., the rate of drug dissolution.
Drug in solid dosage form in GI fluid 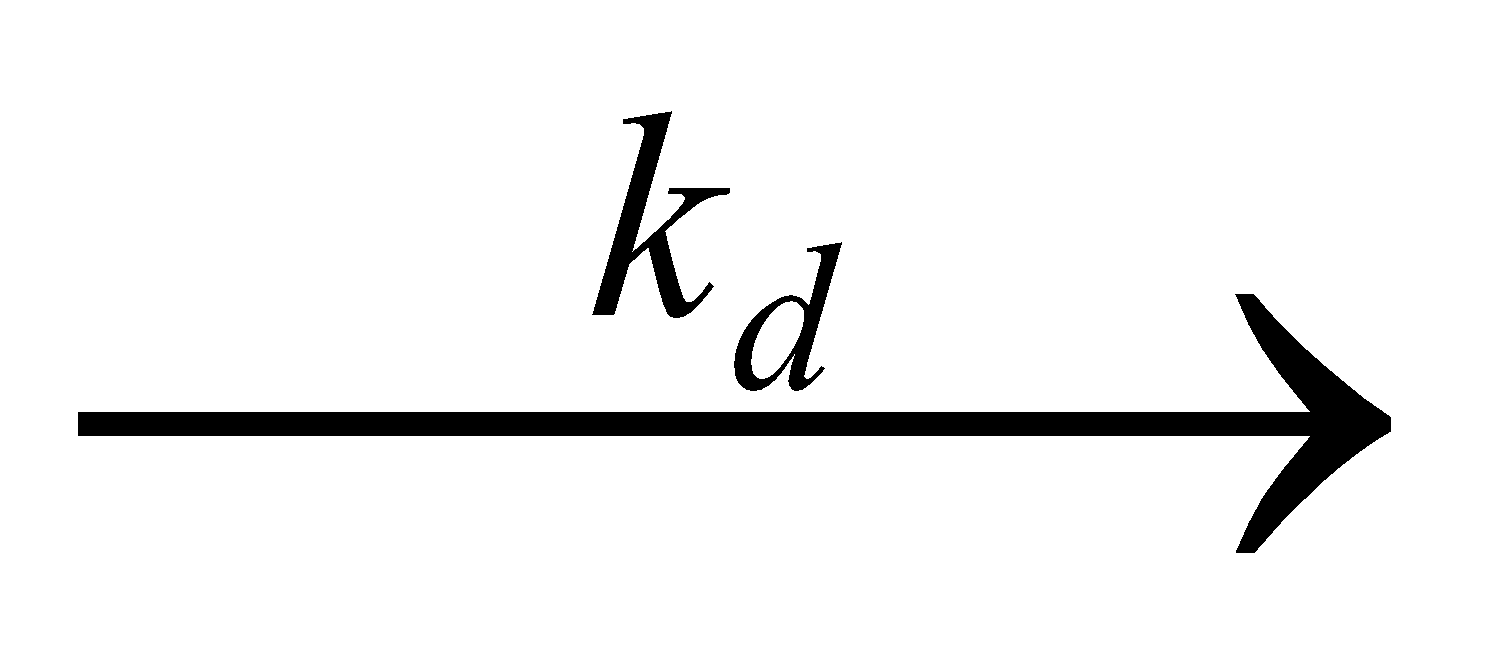 Drug in solution in GI fluid
Drug in solution in GI fluid 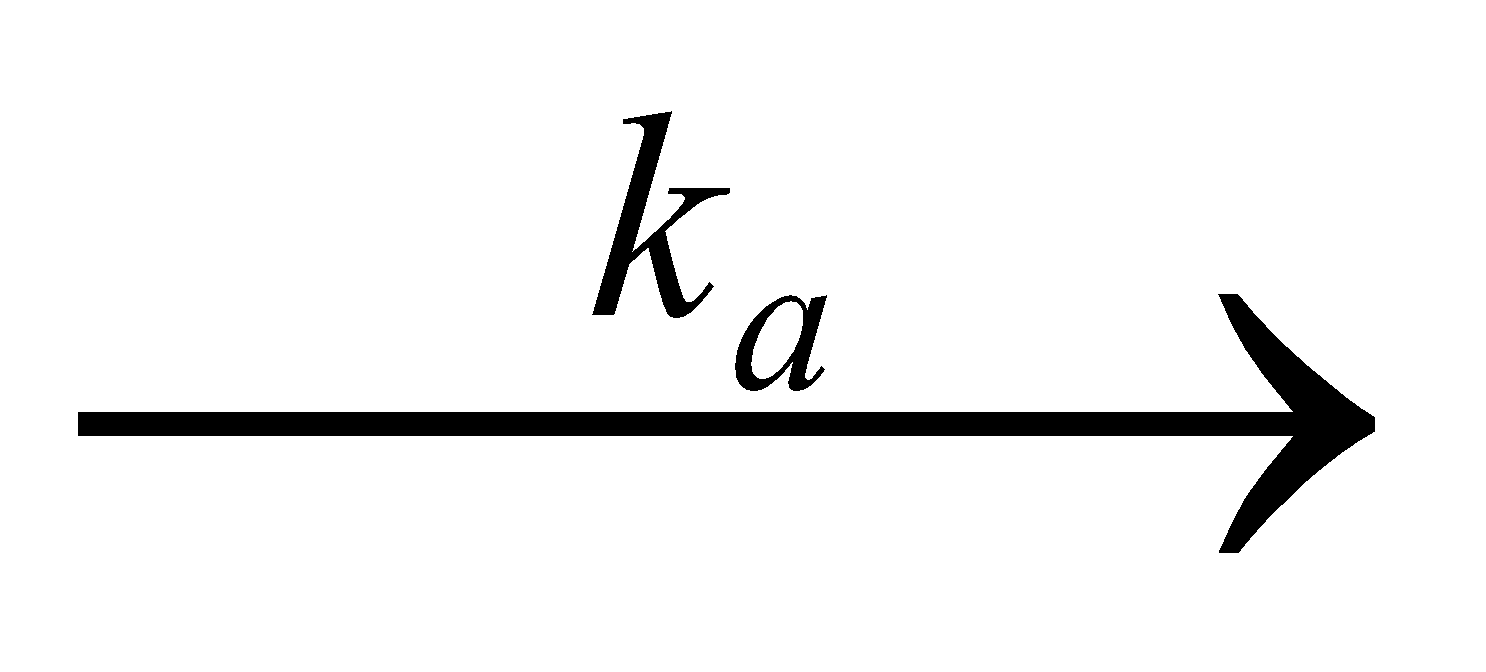
Drug in blood  Elimination
Elimination
Where, kd = Dissolution rate constant
ka = Absorption rate constant
ke = Elimination rate constant
Dissolution analysis of pharmaceutical solid dosage forms have also emerged as a very important test of product quality. The USP has included a test for monitoring drug release from enteric coated table in the gastric simulated fluid (GSF) for 2 hours and intestinal simulated fluid (ISF) for 45 minutes (0.1 N NaOH is used to increase the solubility of the drug in ISF). The test objective includes making sure that, no significant dissolution occurs in the acid phase or in GSF (less than 10% for any sample) and specified percent of drug must be released in the buffer phase (in ISF).
Apparatus:
- USP dissolution apparatus
- Test tube and test tube holder
- Filter paper
- Pipette
- Volumetric flask
- UV-Spectrophotometer (Shimadzu, Model: UV-1200)
Dissolution apparatus: It consists of 1000 ml vessel made of glass or inert transparent material, a paddle with a variable speed motion. For the oral solid dosage form, the motion of paddle is 75 rpm. The vessel can be immersed in a suitable water bath of any convenient size and the temperature is 37 ± 5°C.
Reagents:
- Enteric coated aspirin tablet
- Gastric simulated fluid (GSF)
- Intestinal simulated fluid (ISF)
- Distilled water
- Standard aspirin powder
- 0.1 N NaOH solution
Preparation of GSF: 2 gm of NaCl and 7 ml of concentrated HCl were taken in a beaker containing water. The content was transferred to 1000 ml volumetric flask and the volume was made up to the mark by adding distilled water.
Preparation of ISF: 8.05 gm Na2HPO4 and 1.65 gm NaH2PO4 were taken in a beaker containing distilled water. Then the content was transferred in a volumetric flask and the volume was made 1000 ml by adding sufficient distilled water.
Preparation of 0.1 N NaOH solution: 4 gm of NaOH was taken in 100 ml volumetric flask and the volume was made up to the mark by adding sufficient distilled water.
Procedure:
- 900 ml of GSF was taken in a beaker used in the USP dissolution apparatus and other 100 ml of GSF was kept as the stock GSF solution, which was used to prepare the sample-1 and sample-2.
The water level of the apparatus was adjusted. The beaker was kept in place in the dissolution apparatus and the apparatus switched on so that, the temperature of the GSF raises up to 37 ± 0.5°C.
- When the temperature becomes 37.5°, then one enteric coated tablet was put into the beaker containing GSF. The button of the stirrer was switched on to rotate it and the speed of the paddle was adjusted at 75 rpm.
- After 1 hour, 10 ml of GSF from the beaker of the apparatus was taken into a test tube and 10 ml of stocked GSF was added into the beaker simultaneously. Then the beaker was kept in place and let the apparatus to work for another 1 hour.
- The 10 ml GSF taken from the beaker was filtered and 2 ml of filtrate was taken in another test tube and it was diluted to 5 times to make it 10 ml by the GSF stocked. This is sample-1.
- After two hours, another 10 ml of GSF from the beaker in the apparatus was taken into a test tube and by following the same procedure of step-4, sample-2 was prepared.
- The tablet was transferred immediately from the GSF beaker into the beaker containing 900 ml of ISF (other 100 ml of ISF was kept as the stock ISF solution) and stirrer was fitted and allowed to rotate at 75 rpm, temperature was also maintained at 37.5°C.
- After 5 minutes, 10 ml of ISF from the beaker of the apparatus was taken into a test tube and 10 ml of stocked ISF was added into the beaker simultaneously. The 10 ml ISF which was taken then filtered and 2 ml of filtrate was taken in another test tube and it was diluted to 5 times with 4 ml of ISF and 4 ml of 0.1 N NaOH solution. This is sample-3.
- After another 5 minutes, another 10 ml of GSF from the beaker in the apparatus was taken into a test tube and by following the same procedure of step-7, sample-4 was prepared.
- Preparation of standard solution:
- 100 ml of aspirin powder was dissolved in the ISF and made the volume up to 100 ml by adding required ISF.
- 1 ml, 2 ml, 3 ml and 4 ml of solutions from the above solution in step-a were taken into four different volumetric flask (50 ml each) and made the volume up to 50 ml by adding required ISF. Thus, the concentration of the four standard solutions were 20 μg/ml, 40 μg/ml, 60 μg/ml and 80 μg/ml respectively. The concentration of these solutions was used to make a standard curve.
- Preparation of blank solution:
- GSF blank: About 10 ml of GSF was taken in a test tube.
- ISF blank: About 10 ml of ISF was taken in a test tube.
- (ISF + NaOH) blank: 5 ml of 0.1 N NaOH + 5 ml of ISF.
- Using spectrophotometer, absorbance of all samples, standard and blank solutions were taken at 295 nm.
Data:
For standard solution:
Concentration of solution (μg/ml)
|
Absorbance (λmax = 277 nm)
|
Blank (ISF)
| |
Standard-1 (20 μg/ml)
| |
Standard-2 (40 μg/ml)
| |
Standard-3 (60 μg/ml)
| |
Standard-4 (80 μg/ml)
|
For sample solution:
Concentration of solution (μg/ml)
|
Absorbance (λmax = 277 nm)
|
Blank (GSF)
| |
Sample-1 (after 1 hr)
| |
Sample-2 (after 2 hr)
| |
Blank (ISF + NaOH)
| |
Sample-3 (after 5 min)
| |
Sample-4 (ISF after 10 min)
|
Preparation of standard curve:
Taking the values of the four standard solution on y-axis and the values of concentration on the x-axis, a curve was plotted that was found straight line.
Calculation:
From the standard curve, slope of the straight line can be calculated by the following formula: m = 
where, m = slope
y = absorbance
x = concentration
Concentration of drug in GSF after 1 hour: x = 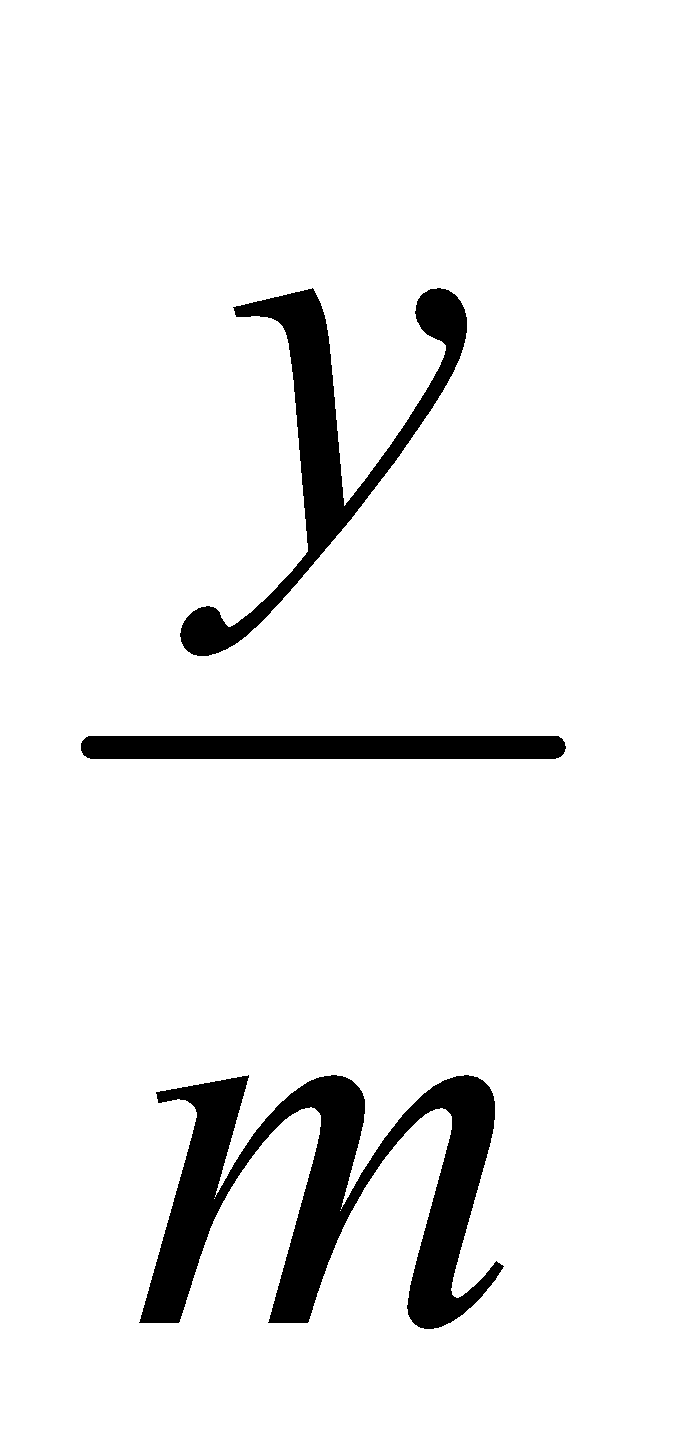 =
=
∴ 900 ml GSF contain = [Dilution factor = 5]
=
=
% of drug release =
Correction value = = μg in 2 ml
= μg in 10 ml
= mg in 10 ml
Concentration of drug in GSF after 2 hour: x = 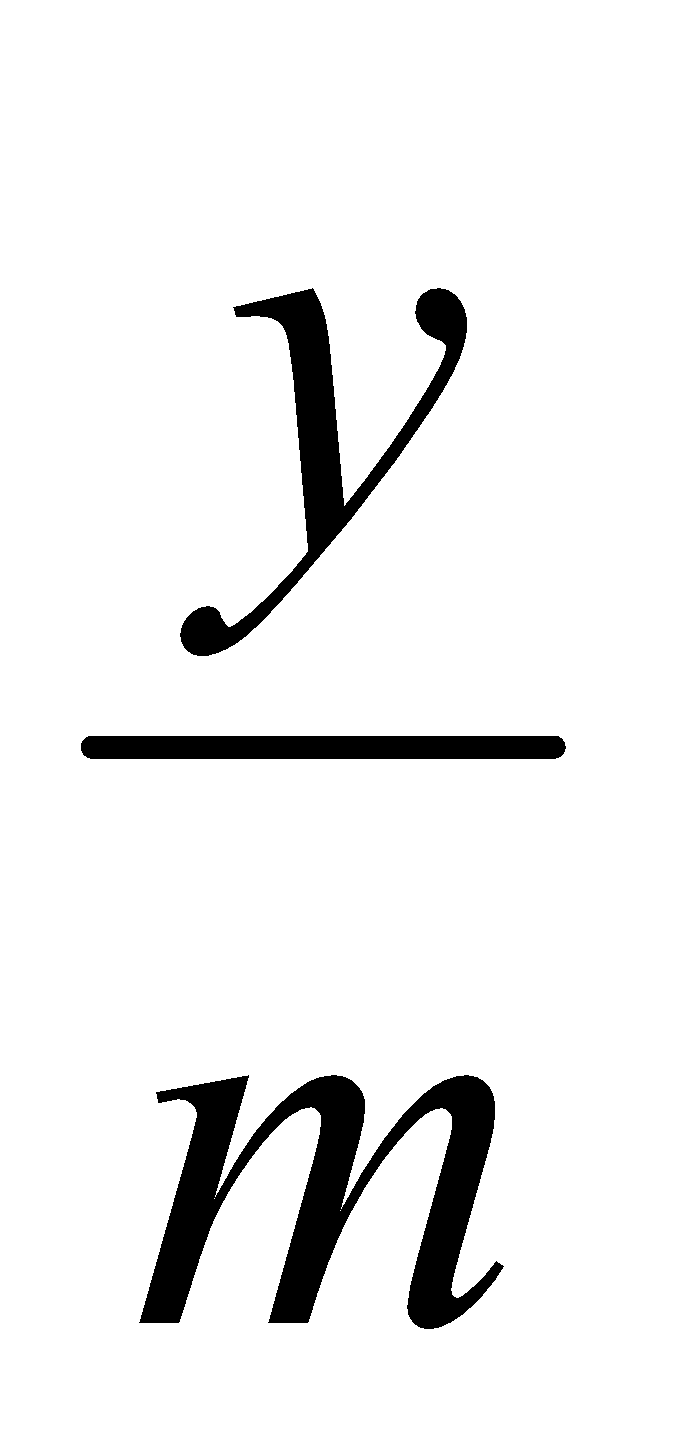 =
=
∴ 900 ml GSF contain = [Dilution factor = 5]
=
=
% of drug release =
Concentration of drug in ISF after 5 minutes: x = 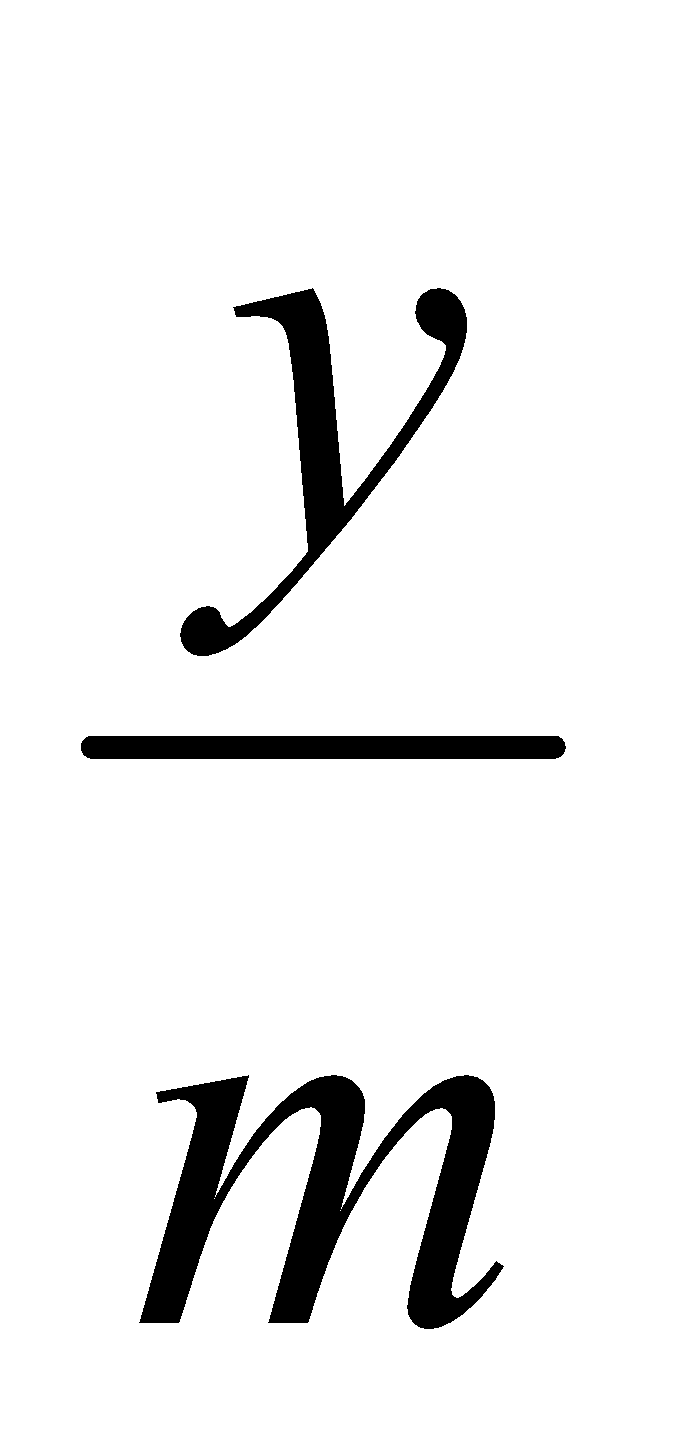 =
=
∴ 900 ml ISF contain = [Dilution factor = 5]
=
=
% of drug release =
Correction value = = μg in 2 ml
= μg in 10 ml
= mg in 10 ml
Concentration of drug in ISF after 10 minutes: x = 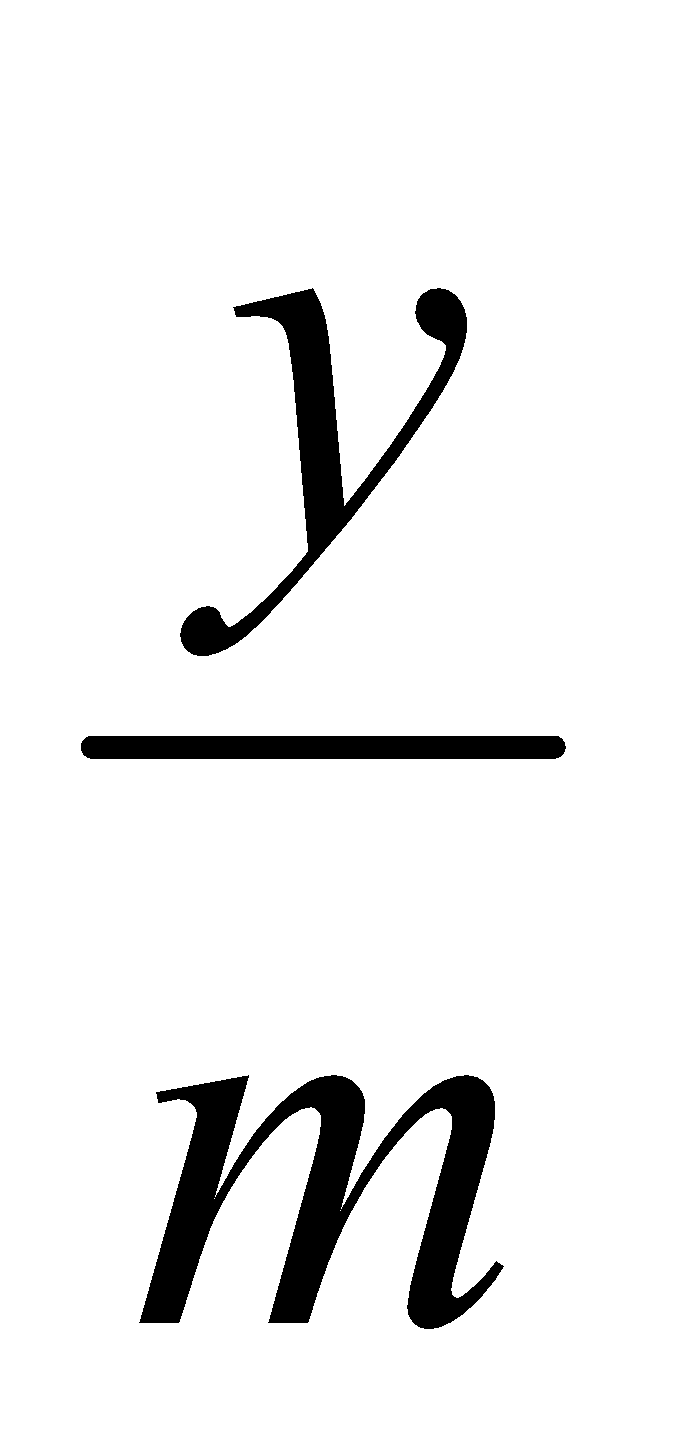 =
=
∴ 900 ml ISF contain = [Dilution factor = 5]
=
=
% of drug release =
Result:
The percentage of release of aspirin in GSF after 1 hour and 2 hours were and , which are very negligible and percent of release of drug in ISF after 5 min and 10 min were and respectively.
Comments:
PDF Link:
No comments:
Post a Comment