Laboratory Manual
Course: 310
Subject: Practical - Bio-Pharmaceutics-I

Course: 310
Subject: Practical - Bio-Pharmaceutics-I
Prepared By
Md. Imran Nur Manik
M.Pharm
Departmnt of Pharmacy
Uniersity of Rajshahi
Md. Imran Nur Manik
M.Pharm
Departmnt of Pharmacy
Uniersity of Rajshahi
Rajshahi-6205, Bangladesh
Available at
Essential Pharma documents
www.pharmacydocs.blogspot.com
Essential Pharma documents
www.pharmacydocs.blogspot.com
INDEX
Serial No.
|
Date
|
Name of the experiment
|
Page No.
|
01
|
Determinations of the uniformity of weight of Paracetamol 500 mg Tablet.
|
02 –03
| |
02
|
Friability test of Paracetamol 500 mg Tablet
|
04 – 04
| |
03
|
Determinations of the Hardness of Paracetamol 500 mg Tablet
|
05 –06
| |
04
|
Determination of Disintegration Time of Paracetamol 500 mg Tablet.
|
07 –07
| |
05
|
Determination of Dissolution Time of Paracetamol 500 mg Tablet.
|
08 –10
|
Experiment Number: 01
|
Date:18.09.2012
|
Name of The Experiment: Determinations of the uniformity of weight of Paracetamol 500 mg Tablet
| |
Principle
The uniformity of tablet dosage form can be demonstrated by either by weight variation or content uniformity test. Weight variation is a compendia test for tablet dosage form and performed when tablets to be tested. A tablet contains 50 mg or more of a single active ingredient comprising 50% or more by weight of the tablet dosage form unit. If the drug forms greater part of the tablet, any variation in the tablet weight obviously indicates a variation in the active ingredient.
Tablet dosage form uniformity by weight variation is determined by selecting not less than 30 tablets form each production batch and weighing accurately at least 10 t5ablets individually and calculating the average weight was followings:-
Average weight= (Total weight of tablets)(Number of Tablets)
i.e. Average weight of Tablets X=(X1+X2+X3+……+Xn)÷ n
Where, n=Total number of tablets weighted.
And,
Percent deviation (error) of a tablet=
i.e. % Deviation=  ……..(i)
……..(i)
Where, i=1, 2, 3…….n
Pharmacopoeal Requirements:
Not more than two of the individual tablet weights deviate from thre3 average weight by more than the specified limit mentioned in the following table and none deviates by more than twice that%.
Pharmacopoea
|
Average weight of Tablet
|
Maximum % Deviation
|
USP
|
Tablet less than 120 mg
|
±10%
|
Range from 120-300 mg
|
±7.5%
| |
More Than 300 mg
|
±5.0%
| |
BP
|
80 mg or Less
|
±10%
|
>80 mg and <250 mg
|
±7.5%
| |
250 mg or more
|
±5.0%
|
Since, the average weight X of Paracetamol500 mg tablet is more than 250 mg
(according to BP) allowed parent deviation should be ±5.0% and not more than two of the individual tablet weights should deviate by ±5.0% and more should deviate by ±10%
Instrumentation:
Electronic Balance
Procedure:
20 tablets were weighted individually .Then the average weigh was calculated and percentage of weight variation was calculated by using the equation ( i) i.e. (Xi-X) 100X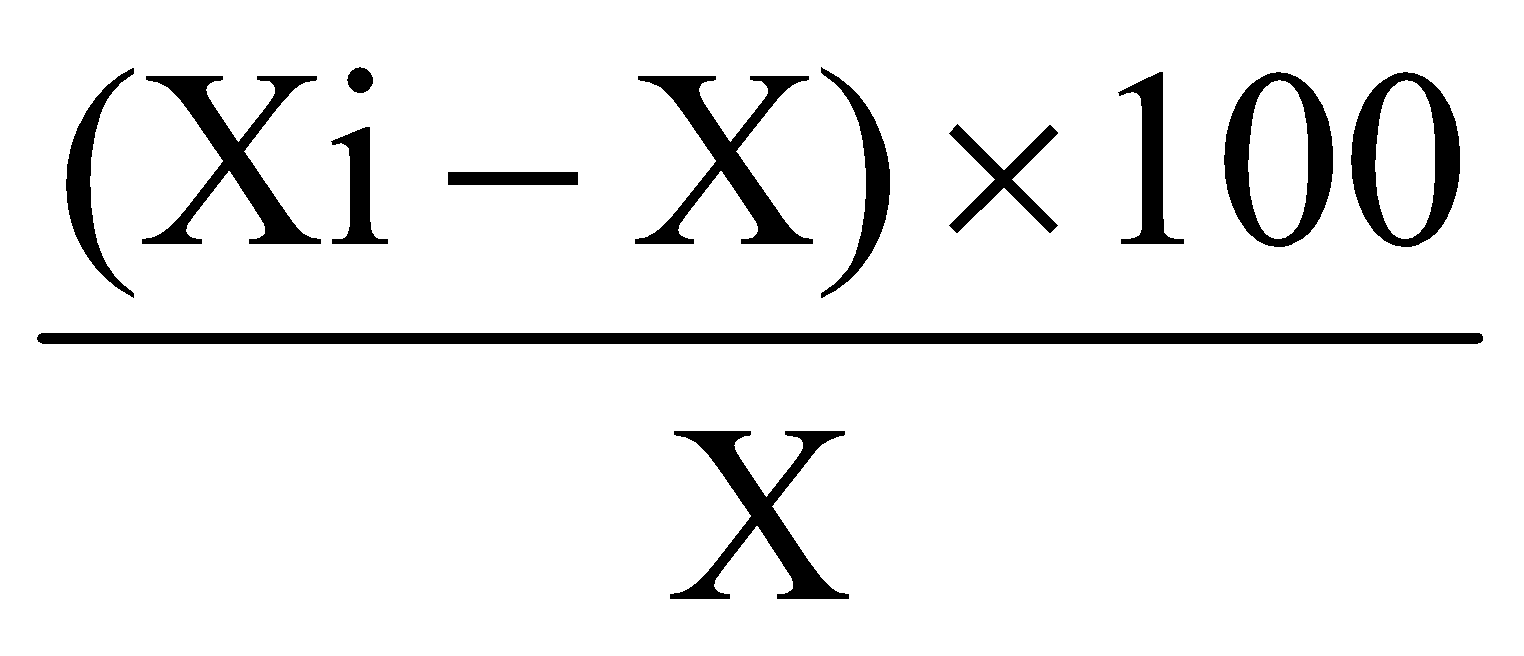
Where, Xi=Sample 1, 2, 3………..20
X=Average weight of 20 tablets.
Data:
Tablet number
(n)
|
Individual weight
(Xi)
|
Average weight
X=(Xi-X) 10020]
|
Percent Deviation
|
1st
| |||
2nd
| |||
3rd
| |||
4th
| |||
5th
| |||
6th
| |||
7th
| |||
8th
| |||
9th
| |||
10th
| |||
11th
| |||
12th
| |||
13th
| |||
14th
| |||
15th
| |||
16th
| |||
17th
| |||
18th
| |||
19th
| |||
20th
|
Total weight=
Test result:
1. The percentage of weight variation ranges from to .
2. Number of Tablet (tablet number……..) deviated by ±5.0% and this deviation (% error….) is less than ±10%.
Comments:
The uniformity of weight if 20 tablets comply with the mentioned specification .So the bath may be declared as passed.
Experiment Number: 02
|
Date:18.09.2012
|
Name of The Experiment: Friability test of Paracetamol 500 mg Tablet
| |
Principle:
Friability is the tendency of tablet to crumble. It is impor4tent for the tablet to resist attrition .Friction and shocks are the forces that most often cause tablets to chip, crack or break. The friability test is designed to evaluate the ability of the tablet to withstand abrasion in packaging, handling and shipping. Another application of friability test is to detect incipient capping or laminate when stressed by attrition inside the rotating cylinder present on the friability tester. It is usually measured by the use of a Roche Friabilitor .A number of tablets is weighted and placed in the apparatus where they are exposed to rolling and repeated shocks as they fall 6 inches in each turn within the apparatus. The value is expressed as percentage.The accepted limit of weight loss after this experiment should not be more than 1 percent% of the total weight of the tablets.
The percent of weight loss can be calculated by using the following formula .
Percentage of weight loss or friability = Initial weight-Final weightIntial weight.
Percentage of weight loss or friability = Initial weight-Final weightIntial weight.
Instrumentation: 1. Electronic Balance
& 2. Roche Friabilitor (which consists of plastic chamber divided into two parts and revolves at a speed of 25 rpm.)
& 2. Roche Friabilitor (which consists of plastic chamber divided into two parts and revolves at a speed of 25 rpm.)
Procedure:
1. Tablets were weighted as not less than 6 gm and taken in the plastic chamber of Friabilator.If the individual weight of tablet is≤600 mg then more than 10 tablets were taken.
2. The chamber was allowed to rotate for about 4 minutes at 25 rpm and then the weight of tablets was taken again. The loss in weight indicates the friability.
3. Finally, The percentage of weight loss was calculated.
Calculation:
Initial weight of tablets =
Final weight of tablets =
Percent loss or Friability tablets = Initial weight-Final weightIntial weight.
=
=
Result:
The Friability of the tablets were found to be = Percent (%) W/W
The Friability of the tablets were found to be = Percent (%) W/W
Comments: The uniformity of weight if 20 tablets comply with the mentioned specification .So the bath may be declared as passed.
Experiment Number: 03
|
Date:18.09.2012
|
Name of The Experiment: Determinations of the Hardness of Paracetamol 500 mg Tablet
| |
Theory:
Tablets should be sufficiently hard to resist breaking during normal, handling, packaging and shipping and must be soft enough to disintegrate properly after swallowing. So the resistance of tablets to capping, abrasion or breaking under conditions of storage, transportation and handling before usage depends on its hardness.
Tablets should be sufficiently hard to resist breaking during normal, handling, packaging and shipping and must be soft enough to disintegrate properly after swallowing. So the resistance of tablets to capping, abrasion or breaking under conditions of storage, transportation and handling before usage depends on its hardness.
Hardness of the tablet is a non-compendial test and is controlled by the degree of the pressure applied during the compression stage. Hardness is an important criterion, since it can affect disintegration and subsequent dissolutuion.If the tablet is too hard, it may not disintegrate in the required period of time to meet the dissolution specifications; if it is too soft it may not be able to withstand the handling during subsequent processing such as coating, packaging and shipping operations.
The test measures crushing strength property; defined as ‘‘the compressional force applied diametrically to a tablet, which just fracture (break) it’’. The force required to break the tablet is measured in kilograms. Force of about 4 kg is considered the minimum requirement for a satisfactory tablet.
Measuring Units:
The moist tablet testing is performed using international system of units. The Newton is the preferred unit of the force as is recognized by the SI system. However the kilogram is also used.
1. Kilogram (Kg): It is the primary unit of mass recognized by SI system.
2. Newton (N): Newton is the SI unit of force and should not be used for tablet hardness testing.
1 Kilogram = 9.807 Newton’s
3.Pound (lb): Technically a unit of mass but can also be used for force. 1 Kilogram = 2.204 Pounds
4.Kilopounds (kp): A unit of force also called kilogram of force.1 Kilopounds =1 kgf.
5. Strong cob (sc): It us an arbitrary unit. 1.4 Strong cob = 1 kg
2. Newton (N): Newton is the SI unit of force and should not be used for tablet hardness testing.
1 Kilogram = 9.807 Newton’s
3.Pound (lb): Technically a unit of mass but can also be used for force. 1 Kilogram = 2.204 Pounds
4.Kilopounds (kp): A unit of force also called kilogram of force.1 Kilopounds =1 kgf.
5. Strong cob (sc): It us an arbitrary unit. 1.4 Strong cob = 1 kg
Interrelationship of the units:
l kg = 9.807 New tons
1 kg = 2.204 pounds
1 kg = 1.4 strong cobs
l kg = 1 kilopond.
Instrument used:
Several devices have been used to test tablet hardness. These include-
- Monsanto hardness tester.
- Pfizer hardness tester
- Strong coble hardness tester.
Monsanto hardness tester is generally used to measure tablet hardness.
Procedure:
The tablet to be tested was held between a fixed and moving tank and the reading of the indicator was adjusted to zero. The force applied to the edge of the tablet was gradually increased by moving screw knob forward until the tablet breaks.
The reading was noted from the scale which indicates the required pressure in kg to break the tablet.
Precaution:
Tablet Hardness may be affected by speed of testing, geometry of the tablet contact points, debris in the testing area, variation in temperature humidity, tablet age etc. so, care should be taken.
Data :
No. of table
|
Hardness in kg
| |
1st Tablet
|
2.5 kg
|
4.5 kg
|
2nd Tablet
|
5.5 kg
|
5.0 kg
|
3rd Tablet
|
6 kg
|
4.5 kg
|
4th Tablet
|
6 kg
|
4.0 kg
|
5th Tablet
|
5 kg
|
5. kg
|
6th Tablet
|
4.6 kg
|
4.5 kg
|
Result:
The range of six readings: 4.6 to 6 kg
Comments: The average hardness of supplied Paracetamil 500 mg was 5.43 kg which is within the expected limit.
Experiment Number: 04
|
Date:18.09.2012
|
Name of The Experiment: Determination of Disintegration Time of Paracetamol 500 mg Tablet.
| |
Theory:
The disintegration test is a measure of the time required under a given set of conditions for a group of tablets to break down into particles which will pass through a 10 mesh screen.
If one or two tablets fail to disintegrate, the test should be repeated using 12 tablets.
Instrumentation:
- Disintegration Tester
- Glass beaker 1 Litre
- Thermometer
The disintegration tester consists of a basket rack holding 6 plastic tubes, open at the top and bottom. The bottom of the lube is covered by a 10-mesh screen. The basket is immersed in a bath of suitable liquid held at 37°C, preferably in a 1 Liter beaker.
Test condition:
1Temperature of simulated Gastric fluid: 37°C ± 0.5 Procedure:
One tablet was placed in each plastic tube and a plastic disc is placed over the tablet. The basket was positioned in one liter beaker containing 900ml gastric simulated fluid at 37°C in such a way that at the highest position of the tube, the screen remains below the surface of liquid surface.
The machine was agitated until the tablet disintegrated. The end point of the lest was achieved when no tablet fragments was remaining on the screen. The time of disintegration was recorded.
Data:
No. of table
|
Disintegration time (min-sec)
| |
1st Tablet
|
6.5 sec
|
1 min 41
|
2nd Tablet
|
68 sec
|
1 min 17
|
3rd Tablet
|
70 sec
|
2.06
|
4th Tablet
|
72 sec
|
1.38
|
5th Tablet
|
75 sec
|
1.34
|
6th Tablet
|
77 sec
|
2.50
|
Result:
The disintegration time of the supplied tablets ranges from 65 sec to 77 sec.
Experiment Number: 05
|
Date:18.09.2012
|
Name of The Experiment: Determination of Dissolution Time of Paracetamol 500 mg Tablet.
| |
Theory:
When a drug administered orally in the form of tablet, the rate of absorption is often controlled how fast the drag is dissolved in GIT fluid of the absorption site.
Drug in solid dosage form in GIT fluid  drug in solution→Drug in blood→Elimination GIT fluid.
drug in solution→Drug in blood→Elimination GIT fluid.
Here Kd represents the rate constant governing dissolution of drug in the GI fluid very often Ka>>Kd and dissolution is the rate limiting step in the overall absorption process. As a result, the onset intensity and the duration of action as well as the extent of drug absorption or bioavailability may be altered by change in the dissolution rate.
The objective of in vitro dissolution test is as follows-
- Whether the drug release is 100% or not.
- Whether the rate of drug dissolution is uniform from batch to batch or not.
- According to BP and USP the range of percentage release of drug should be ±5%.
Apparatus:
- USP dissolution lest apparatus
- Test tube rack
- Filter paper
- Pipette.
- Volumetric flask
- Measuring flask
- Spcctrophotometer.
USP dissolution test apparatus:
It consists of 1000ml vessel made up of glass or inert transparent material, a variable speed motor and a cylindrical dissolution basket. The vessel can be immerged in a suitable water bath at any contention at size that permits keeping the water continuously in motion and holding the temperature at 37±().5()°c. The basket is detectable and made up of'16 mesh stainless steel set formed into cylinder 3.66cm height of 25 cm in diameter.
Reagents:
- Gastric simulated fluid
- N/10 NaOH solution
- Distilled water
Preparation of simulated gastric fluid:
2gm of NaCl and 7 ml of cone, MCI taken in a large beaker containing distilled water then the content was transferred in a volumetric flask and the final volume was made 1000 ml by adding sufficient distilled wetter.
Procedure:
1. The beaker was filled with 1000ml gastric simulated fluid and the fluid was heated up to 37°c by adjusting temperature.
- The tablet was put into the beaker and the instrument was stirred immediately the speed of the stirrer was 50 rpm.
- After 30 minutes l0 ml of sample from the beaker was taken in a test tube and was filtered.
- 2 ml of filtrate was taken and 0.1N NaOH was added to it up to 100ml &s it sample solution.
Preparation of blank solution:
2 ml of gastric simulated fluid was taken in to 100 ml volumetric flask and 0.1N NaOH added it to make. It was the blank solution.
Preparation of standard solution:
Each paracetamol tablet contains 500mg active ingredient pracelamol BP. A tablet was dissolved in 100.0 ml fluid. So, 1000 ml fluid contains 500 mg of paracetamol
1 ml fluid contain = mg of paracetamol
100 ml fluid contain =  mg of paracetamo
mg of paracetamo
= 50gm of paracetamol
Approximately 50mg (0.0gm) paracetamol was dissolved in gastric fluid was made the 100 ml with it. 10 ml was taken from the solution and was filtered.
From the filtrate 2ml was taken in a measuring cylinder and 0.1N NaOH and added to make the volume 100 ml. It was the/standard solution.
Now the absorbance of blank solution sample solution & standard solution were taken at 254 nm in a spectrophotometer.
At first the absorbance of the blank solution were taken and the apparatus was done at auto zero. So, this reading was not necessary.
After this reading the absorbance of sample standard was taken then, the percentage of content of paracetamol in the solution was calculated.
1000 ml simulated fluid conation = 500 mg of paracetamol
1 ml simulated fluid contain =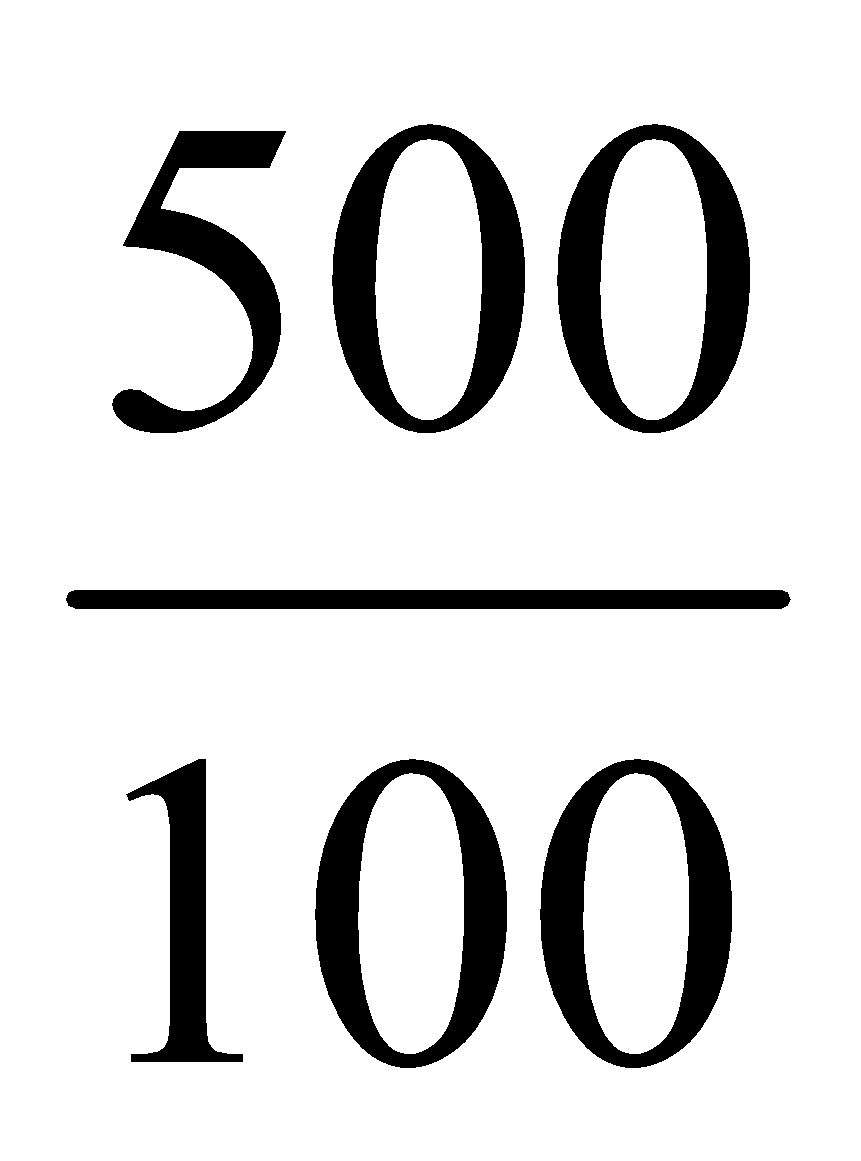 mg of paracetamol
mg of paracetamol
= 0.5 gm of paracetamol
Therefore, the concentration of standard solution was 0.5 mg/ml of pracetamol.
Concentration of sample solution can be calculated by using following formula
Where, Cs is concentration of sample solution = 0.4646 mg/ml.
Concentration of standard solution, Csd = 0.5 mg/ml
Absorbance of sample solution, As = 0.605
Absorbance of sample solution, Asd = 0.651
Now,
1 ml fluid contain = 0.4646
1000 ml fluid contain = 0.4646×1000
We know that, = 646.6 mg
% Release of drug = 
Result:
Percentage release of peacetime was 92.93%
PDF Link:
No comments:
Post a Comment